Different Types of Numbers
In mathematics there are different types of numbers, each with a unique place in the numeric family tree.
Table of Contents
A Family Tree of Numbers
Let’s start by defining the different categories of numbers:
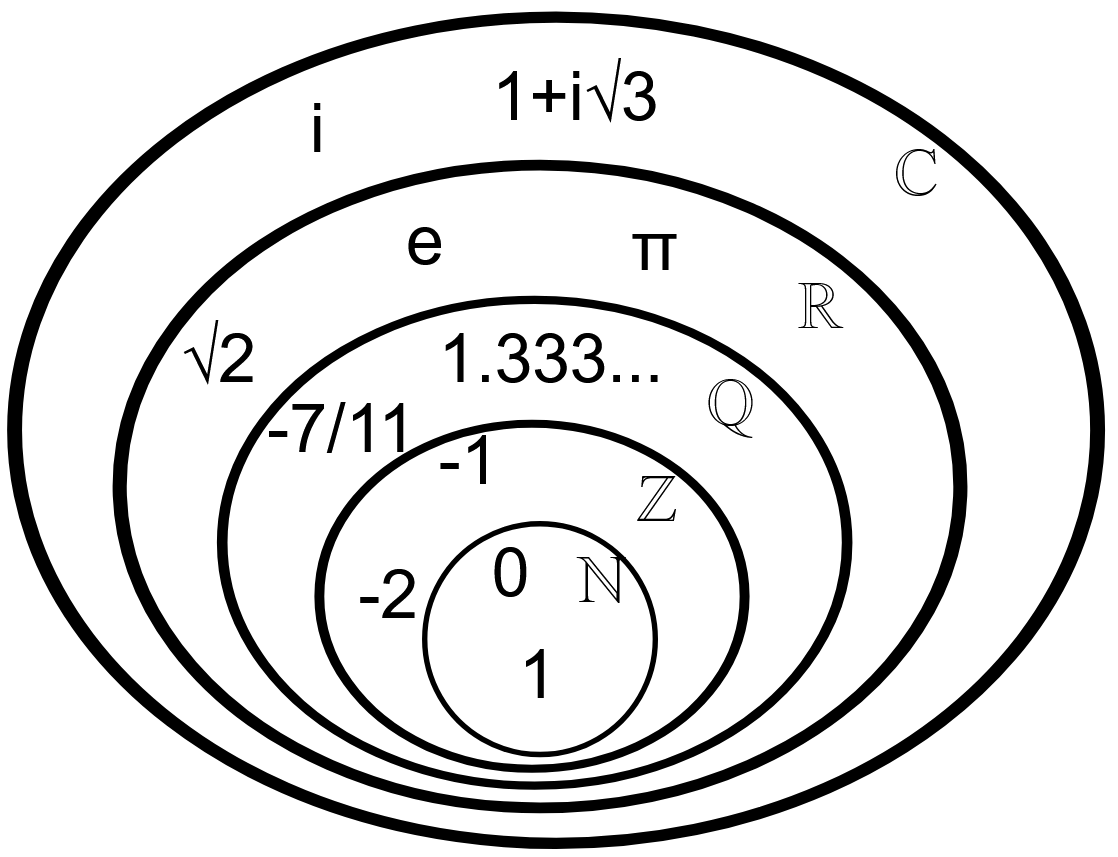
- Natural Numbers: Also known as the counting numbers, these are the positive integers starting at 1. ℕ = {1, 2, 3, 4, …}
- Whole Numbers: The natural numbers, but including zero. 𝕎 = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, …}
- Integers: The whole numbers, but including all negative versions. ℤ = { …, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …}
- Rational Numbers: Any number that can be written as a ratio of two numbers in the form p/q, where both p and q are natural numbers. ℚ is used represent the rationals.
- Irrational Numbers: Any number that cannot be expressed as the ratio of one over another. These numbers where their fractional component extends forever in a non-repeating sequence. ℝ-ℚ is sometimes used to represent the irrationals. Examples include π and the square root of 2.
- Real Numbers: Any number that can represent a distance on a number line. The reals (ℝ) include all integer, rational, and irrational numbers.
- Imaginary Numbers: Numbers that are the product of a real number and the imaginary unit i, where i is defined to be the square root of -1.
- Complex Numbers: Number of the form a+bi where “a and b” are real numbers and “i” is the imaginary unit defined above. The set of all complex numbers is represented by ℂs.
Visual Subsets of Numbers
🎵 Note:
Image combines the whole numbers (𝕎) with the natural numbers (ℕ).
Number Types Videos
A slightly different way of looking at this (without the inclusion of the imaginary numbers):